What are the Factors Affecting the Life of a Lead Acid Battery?
I've seen countless batteries fail prematurely due to improper maintenance and usage. Understanding what affects battery life can help prevent costly replacements and system failures.
The main factors affecting lead acid battery life include storage conditions, discharge depth, charging practices, operating temperature, and sulfation. Proper maintenance and operating conditions can significantly extend battery lifespan and maintain capacity.

Let's explore these critical factors in detail to help you maximize your battery's service life and performance.
What is the Biggest Cause of Lead-acid Battery Failures?
Many battery users focus on various maintenance aspects, but there's one primary culprit behind most battery failures that often goes unaddressed.
Battery sulfation is the biggest cause of lead-acid battery failures. This occurs when lead sulfate crystals form on battery plates due to prolonged discharge states, inadequate charging, or irregular use, preventing normal chemical reactions.

From our experience dealing with failed batteries, here's a detailed breakdown of how sulfation impacts battery life:
Understanding Battery Sulfation
-
Formation Process
- Discharge creates lead sulfate
- Normal charging converts it back
- Extended discharge allows crystallization
- Crystals become permanent and reduce capacity
-
Contributing Factors
- Long storage without charging
- Partial state of charge operation
- High temperature exposure
- Inadequate charging voltage
The impact of sulfation1 is particularly severe because:
- It reduces the active material available for reactions
- Increases internal resistance2
- Decreases charging efficiency
- Leads to permanent capacity loss
What are the Factors Influencing the Capacity of Lead-acid Batteries?
Understanding capacity influencing factors is crucial for maintaining optimal battery performance in any application.
Battery capacity is primarily influenced by discharge rate, temperature, age, charging method, and maintenance practices. These factors affect the battery's ability to deliver its rated capacity and maintain performance over time.

Here's our analysis of the key factors based on years of battery testing and monitoring:
Critical Capacity Factors
| Factor | Impact | Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | ±0.5% capacity per °C | Maintain 20-25°C |
| Discharge Rate | Higher rates reduce capacity | Match load to battery rating |
| Age | Natural capacity decline | Regular maintenance |
| Charging Method | Affects charge acceptance | Use proper charging profile |
| State of Charge | Affects available capacity | Avoid deep discharge |
What are the Common Problems Associated with Lead-acid Batteries?
After years of troubleshooting battery issues, I've identified recurring problems that affect most lead-acid battery installations.
Common problems include premature capacity loss, terminal corrosion, internal short circuits, case bulging, and electrolyte stratification. Many of these issues stem from improper maintenance or operating conditions.
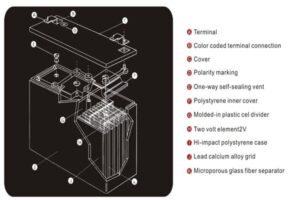
Let's examine these problems and their solutions:
Common Battery Issues Analysis
- Physical Problems
- Terminal corrosion reduces connection quality[^3]
- Case bulging indicates overcharging
- Cracked cases from freezing or impact
- Loose internal connections from vibration
-
Chemical Issues
- Electrolyte stratification in tall cells
- Active material shedding
- Grid corrosion from overcharging
- Sulfation from undercharging
-
Performance Problems
- Reduced capacity
- High self-discharge
- Poor charge acceptance
- Increased internal resistance
What is the Main Reason Lead-acid Batteries Break Down and Lose Capacity?
Through numerous battery failure analyses, I've identified the fundamental cause of battery degradation and capacity loss.
The main reason for battery breakdown is the progressive deterioration of the active material on the plates, primarily caused by sulfation and physical degradation. This process accelerates under poor operating conditions and inadequate maintenance.

Understanding the breakdown process helps prevent premature failure:
Battery Degradation Factors
-
Chemical Degradation
- Sulfation crystallization
- Grid corrosion
- Active material transformation
- Electrolyte decomposition
-
Physical Degradation
- Plate material shedding
- Grid growth
- Separator deterioration
- Internal short circuits
The combined effect of these factors leads to:
- Reduced active material
- Increased internal resistance
- Decreased charge acceptance
- Ultimate battery failure
Conclusion
To maximize lead-acid battery life, focus on preventing sulfation through proper charging, maintaining optimal temperature, and regular maintenance. Understanding and addressing these factors can double or triple your battery's service life.