Lead Acid vs Lithium Ion, Which One is Better?
After installing and maintaining both types of batteries for years, I've seen many users struggle with this choice. The wrong decision can lead to unexpected costs and safety concerns.
The choice between lithium-ion and lead acid batteries depends on specific needs. Lithium-ion offers longer life and better performance but at higher cost, while lead acid provides better safety and recyclability at lower initial investment.
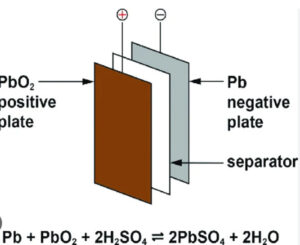
Let's explore these differences in detail to help you make an informed decision that balances performance, cost, and safety.
Which is Better, Lead Acid or Lithium-ion?
The debate between these technologies often sparks heated discussions among professionals. Each has distinct advantages that make them suitable for different applications.
Lithium-ion batteries excel in performance with higher energy density and longer lifespan, while lead acid batteries offer better safety features and easier recycling processes. The choice depends on your specific requirements.
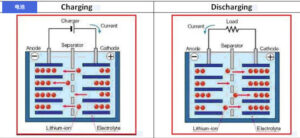
Here's my detailed analysis based on extensive experience:
Comprehensive Comparison
-
Cost Considerations
- Initial investment: Lead acid is 50-70% cheaper
- Maintenance costs1: Lithium requires less maintenance
- Replacement frequency: Lead acid needs more frequent replacement
- Recycling costs: Lead acid recycling is more economical
- Operating costs: Lithium has better efficiency
-
Safety Aspects
- Fire risk: Lead acid is more stable
- Thermal runaway: Higher risk with lithium
- Ventilation requirements: Lead acid needs more
- Transportation restrictions: Stricter for lithium
- Installation requirements: More complex for lithium
- Environmental Impact
- Recyclability rate: Lead acid >95%, Lithium <5%
- Raw material availability
- Manufacturing carbon footprint
- End-of-life disposal
- Environmental hazards
Which Lasts Longer Lead Acid or Lithium?
This question comes up frequently in my consultations with clients looking for long-term power solutions.
Lithium-ion batteries typically last 8-15 years with 3000-7000 cycles, while lead acid batteries usually last 5-10 years with 200-300 cycles. However, proper maintenance can significantly extend lead acid battery life.
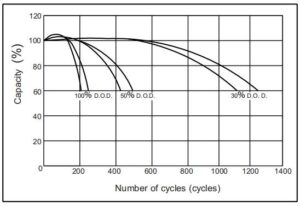
Let me share what I've learned about longevity factors:
Lifespan Influencing Factors
-
Usage Patterns
- Depth of discharge impact
- Charging frequency
- Temperature exposure
- Load characteristics
- Maintenance schedule
-
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature range tolerance
- Humidity effects
- Installation location impact
- Ventilation requirements
- Storage considerations
Is Lead Acid or Lithium Better for UPS?
Through my experience with UPS installations, I've learned that this choice significantly impacts system reliability and cost.
For UPS applications, lead acid batteries often prove more practical due to their lower cost, better safety profile, and established recycling infrastructure. However, lithium-ion can be advantageous in space-constrained or high-cycle applications.

Here's my analysis of UPS-specific considerations:
UPS Application Factors
-
Performance Requirements
- Backup duration needs
- Response time requirements
- Space constraints
- Maintenance accessibility
- Replacement logistics
-
Cost Considerations
- Initial investment
- Installation costs
- Maintenance expenses
- Replacement cycles
- Disposal fees
Which Type of Battery is Best?
Having worked with various battery technologies, I've found that the "best" battery depends entirely on specific use cases and requirements.
The optimal choice varies by application. Lead acid excels in safety-critical, cost-sensitive applications, while lithium-ion is superior for high-performance, space-constrained situations requiring longer life cycles.

Consider these key factors I've identified:
Selection Criteria
-
Application Requirements
- Operating environment
- Performance needs
- Safety considerations
- Maintenance capability
- Budget constraints
-
Life Cycle Analysis
- Initial costs
- Operating expenses
- Maintenance requirements
- Replacement frequency
- Disposal costs
Conclusion
While lithium-ion batteries offer superior performance and longevity, lead acid batteries excel in safety and recyclability. Your choice should balance performance needs, budget constraints, safety requirements, and environmental considerations.
-
Learn about the maintenance requirements and costs of different battery types to optimize your investment and operational efficiency. ↩