What is the difference between VRLA and AGM batteries?
In my years of working with batteries, I've noticed a lot of confusion about VRLA and AGM technologies. This confusion can lead to improper battery selection and maintenance issues.
VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) is a category of sealed lead-acid batteries that includes AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) as its most common type. While all AGM batteries are VRLA batteries, not all VRLA batteries are AGM batteries.
VRLA and AGM battery types
Let's dive into the details to understand these technologies better and clear up some common misconceptions.
Are VRLA and AGM the same?
I often get this question from customers looking to replace their batteries, and the answer reveals an important technical distinction.
While AGM batteries are a type of VRLA battery, they're not exactly the same. AGM is currently the dominant VRLA technology, having largely replaced traditional flooded lead-acid and gel VRLA batteries in most applications.

Here's what I've learned about the relationship between these technologies:
Understanding the Hierarchy
-
VRLA Classification
- Acts as the parent category
- Includes multiple battery types
- Features valve regulation
- Maintenance-free design1
- Sealed construction
-
AGM Specifics
- Most common VRLA type
- Uses glass mat separators
- Superior performance
- Better charge efficiency
- Improved safety features
-
Market Evolution
- Increasing AGM dominance
- Declining gel VRLA usage
- Technological improvements
- Cost optimization
- Application expansion
Can I charge a VRLA battery with an AGM charger?
This question comes up frequently in my battery installation work, and it's crucial for maintaining battery life.
Yes, you can charge a VRLA battery with an AGM charger since AGM is a type of VRLA battery. However, it's important to ensure the voltage and current specifications match your specific battery's requirements.
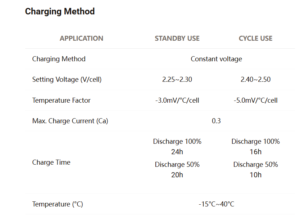
Let me share my charging recommendations based on extensive experience:
Charging Considerations
-
Voltage Requirements
- Float voltage settings
- Bulk charging parameters
- Temperature compensation
- Charging stages1
- Current limitations
-
Safety Precautions
- Ventilation needs
- Temperature monitoring
- Overcharge protection
- Connection security
- Environmental factors
What does VRLA mean on a battery?
Understanding this terminology helps in making informed decisions about battery selection and maintenance.
VRLA stands for Valve Regulated Lead Acid, indicating a sealed battery design with pressure relief valves. This technology eliminates regular water maintenance and allows for safer, position-flexible installation.

Here's my breakdown of VRLA technology's key aspects:
VRLA Technology Explained
-
Design Features
- Sealed construction
- Pressure regulation
- Internal gas recombination
- Maintenance-free operation
- Position flexibility
-
Operating Principles
- Oxygen recombination
- Pressure management
- Electrolyte containment
- Safety mechanisms
- Environmental protection
Is a VRLA battery better?
Based on my installation and maintenance experience, this question requires considering specific application needs.
VRLA batteries, particularly AGM types, are generally better for modern applications due to their maintenance-free operation, safer design, and installation flexibility. They've become the standard choice for most backup power systems.

Let me share my insights on VRLA advantages:
VRLA Benefits Analysis
-
Practical Advantages
- Maintenance-free operation
- Installation flexibility
- Reduced gas emission
- Improved safety
- Better reliability
-
Application Suitability
- UPS systems
- Solar storage
- Telecommunications
- Emergency lighting
- Medical equipment
-
Modern Developments
- Enhanced performance
- Longer service life
- Better charge acceptance
- Improved reliability
- Advanced monitoring capabilities
-
Market Evolution
- Growing AGM adoption
- Declining flooded battery use
- Technology improvements
- Cost optimization
- Application expansion
Current Trends
-
Industry Shift
- Increasing AGM dominance
- Phase-out of older technologies
- Enhanced manufacturing processes
- Quality improvements
- Cost reductions
-
Future Outlook
- Continued AGM growth
- Technology refinements
- Performance enhancements
- Application expansion
- Market consolidation
Conclusion
Today's VRLA batteries are predominantly AGM type, offering superior performance and safety. This evolution reflects the industry's move toward more efficient, maintenance-free solutions, making AGM-VRLA the preferred choice for most modern applications.